LISTEN TO THIS ARTICLE
Electronic invoices, or e-invoices, are digital versions of traditional paper invoices. They contain the same information as paper invoices but are exchanged in a standardized electronic format. The use of e-invoices can significantly reduce paperwork, speed up transactions, and improve overall business efficiency. However, for these benefits to be realized, a reliable and standardized method of exchanging e-invoices is necessary. This is where the 4-Corner Model comes into play.
What is the 4-Corner Model?
The 4-Corner Model is a standardized framework for the exchange of e-invoices between businesses. It is called the 4-Corner Model because it involves four key participants or "corners":
1. Supplier
2. Supplier's Access Point
3. Buyer's Access Point
4. Buyer
Why is it Called the 4-Corner Model?
Each participant represents a corner of the model, creating a reliable and secure pathway for the transmission of e-invoices. This ensures that the supplier and buyer do not need to have direct interaction with each other's systems, simplifying the process and enhancing security.
How the 4-Corner Model Works
Let's break down the roles of each corner:
1. Supplier : Supplier generates the e-invoice and sends it to their access point.
2. Supplier's Access Point : The supplier's access point receives the e-invoice and validates it. This access point acts as an intermediary, ensuring the invoice is correctly formatted and contains all necessary information.
3. Buyer's Access Point : The buyer's access point receives the validated e-invoice from the supplier's access point. It then forwards the e-invoice to the buyer, ensuring it meets all their requirements.
4. Buyer : The buyer receives the e-invoice from their access point and processes it for payment.
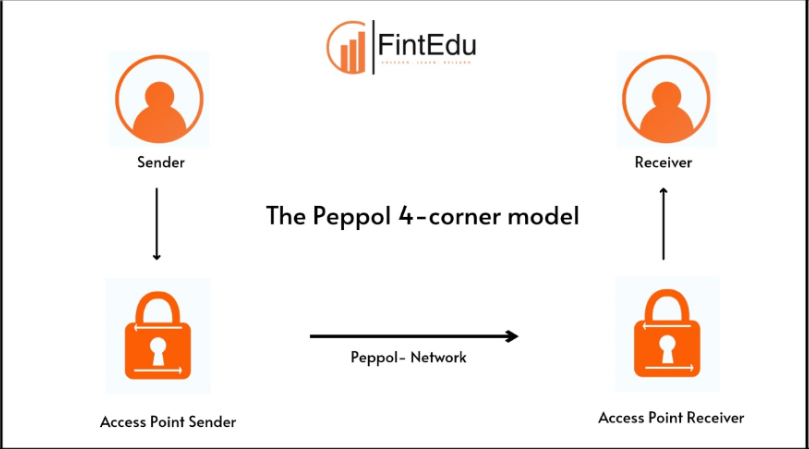
This process ensures that both parties use their respective access points for e-invoice exchange, making the system efficient and secure.
Benefits of the 4-Corner Model
Efficiency
- Streamlined Process: Automating the invoicing process reduces the time required for manual handling.
- Faster Transactions: E-invoices are processed quicker than paper invoices, speeding up the payment cycle.
Error Reduction
- Accuracy: Automated validation at the access points reduces the likelihood of errors.
- Consistency: Standardized formats ensure consistent data exchange.
Security
- Data Integrity: E-invoices are less prone to tampering compared to paper invoices.
- Confidentiality: Secure transmission channels protect sensitive financial information.
Scalability
- Adaptability: The model can accommodate businesses of all sizes.
- Interoperability: Works across different systems and platforms, facilitating global trade.
The 4-Corner Model was popularized and implemented by PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement Online) - a network that facilitates electronic procurement and invoicing across Europe. It provides the infrastructure and standards necessary for the 4-Corner Model, ensuring interoperability and compliance across different systems and countries. PEPPOL's role is crucial in promoting the adoption of e-invoicing, making cross-border transactions more accessible for businesses of all sizes.
Disclaimer: Content posted is for informational and knowledge sharing purposes only, and is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice related to tax, finance or accounting. The view/interpretation of the publisher is based on the available Law, guidelines and information. Each reader should take due professional care before you act after reading the contents of that article/post. No warranty whatsoever is made that any of the articles are accurate and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for tax or accounting advice.
Related Articles
Basics of E-invoicing - Series 1
Basics of E-invoicing – Series 2
Basics of E-invoicing – Series 3
Technical and Process Challenges in E-invoicing